Ficheiro:Transmission line animation open short2.gif
O conteúdo da página não é suportado noutras línguas.
Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre.
Transmission_line_animation_open_short2.gif (300 × 110 píxeis, tamanho: 105 kB, tipo MIME: image/gif, cíclico, 50 quadros, 2,5 s)
|
|
Esta imagem provém do Wikimedia Commons, um acervo de conteúdo livre da Wikimedia Foundation que pode ser utilizado por outros projetos.
|
Descrição do ficheiro
| DescriçãoTransmission line animation open short2.gif |
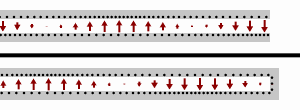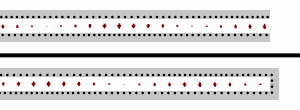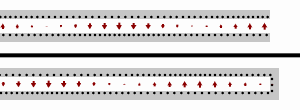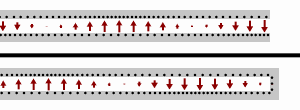
English: Two transmission lines, the top one terminated at an open-circuit, the bottom terminated at a short circuit. Black dots represent electrons, and the arrows show the electric field. |
| Data | |
| Origem | Obra do próprio |
| Autor | Sbyrnes321 |
Licenciamento
Eu, titular dos direitos de autor desta obra, publico-a com a seguinte licença:
| A utilização deste ficheiro é regulada nos termos Creative Commons - CC0 1.0 Dedicação Universal ao Domínio Público. | |
| A pessoa que associou uma obra a este documento dedicou-a ao domínio público, renunciando a todos os seus direitos sobre a obra em todo o mundo ao abrigo da legislação de direitos de autor, incluindo a todos os direitos legais conexos, na medida permitida por lei. Pode copiar, modificar, distribuir e executar a obra, até com fins comerciais, sem pedir autorização.
http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.enCC0Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedicationfalsefalse |
Source code
"""
(C) Steven Byrnes, 2014-2016. This code is released under the MIT license
http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT
This code runs in Python 2.7 or 3.3. It requires imagemagick to be installed;
that's how it assembles images into animated GIFs.
"""
# Use Python 3 style division: a/b is real division, a//b is integer division
from __future__ import division
import subprocess, os
directory_now = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
import pygame as pg
from numpy import pi, linspace, cos, sin
frames_in_anim = 50
animation_loop_seconds = 2.5 #time in seconds for animation to loop one cycle
bgcolor = (255,255,255) #background is white
ecolor = (0,0,0) #electrons are black
wire_color = (200,200,200) # wire color is light gray
split_line_color = (0,0,0) #line down the middle is black
arrow_color = (140,0,0) #arrows are red
# pygame draws pixel-art, not smoothed. Therefore I am drawing it
# bigger, then smoothly shrinking it down
img_height = 330
img_width = 900
final_height = 110
final_width = 300
# ~23 megapixel limit for wikipedia animated gifs
assert final_height * final_width * frames_in_anim < 22e6
# transmission line wire length and thickness, and y-coordinate of the top of
# each wire
tl_length = int(img_width * .9)
tl_thickness = 27
tl_open_top_y = 30
tl_open_bot_y = tl_open_top_y + 69
tl_short_top_y = 204
tl_short_bot_y = tl_short_top_y + 69
tl_open_center_y = int((tl_open_top_y + tl_open_bot_y + tl_thickness) / 2)
tl_short_center_y = int((tl_short_top_y + tl_short_bot_y + tl_thickness) / 2)
wavelength = 1.1 * tl_length
e_radius = 4
# dimensions of triangular arrow head (this is for the longest arrows; it's
# scaled down when the arrow is too small)
arrowhead_base = 9
arrowhead_height = 15
# width of the arrow line
arrow_width = 6
# number of electrons spread out over the transmission line (top plus bottom)
num_electrons = 100
# max_e_displacement is defined here as a multiple of the total electron path length
# (roughly twice the width of the image, because we're adding top + bottom)
max_e_displacement = 1/40
num_arrows = 20
max_arrow_halflength = 18
def tup_round(tup):
"""round each element of a tuple to nearest integer"""
return tuple(int(round(x)) for x in tup)
def draw_arrow(surf, x, tail_y, head_y):
"""
draw a vertical arrow. Coordinates do not need to be integers
"""
# calculate dimensions of the triangle; it's scaled down for short arrows
if abs(head_y - tail_y) >= 1.5 * arrowhead_height:
h = arrowhead_height
b = arrowhead_base
else:
h = abs(head_y - tail_y) / 1.5
b = arrowhead_base * h / arrowhead_height
if tail_y < head_y:
# downward arrow
triangle = [tup_round((x, head_y)),
tup_round((x - b, head_y - h)),
tup_round((x + b, head_y - h))]
triangle_middle_y = head_y - h/2
else:
# upward arrow
triangle = [tup_round((x, head_y)),
tup_round((x - b, head_y + h)),
tup_round((x + b, head_y + h))]
triangle_middle_y = head_y + h/2
pg.draw.line(surf, arrow_color, tup_round((x, tail_y)),
tup_round((x, triangle_middle_y)), arrow_width)
pg.draw.polygon(surf, arrow_color, triangle, 0)
def e_path_open(param, time):
"""
"param" is an abstract coordinate that goes from 0 to 1 as the electron
position goes right across the top wire then left across the bottom wire.
"time" goes from 0 to 2pi over the course of the animation.
This returns a dictionary: 'pos' is (x,y), the
coordinates of the corresponding point on the electron
dot path; 'displacement' is the displacement of an electron at this point
relative to its equilibrium position (between -1 and -1); and 'charge' is
the net charge at this point (between -1 and +1)
This is for the open-circuit line.
"""
# d is a vertical offset between the electrons and the wires
d = e_radius + 2
# pad is how far to extend the transmission line beyond the image borders
# (since those electrons may enter the image a bit)
pad = 36
path_length = 2 * (tl_length + pad)
howfar = param * path_length
#go right along top transmission line
if howfar < tl_length + pad:
x = howfar - pad
y = tl_open_top_y + tl_thickness - d
displacement = -sin(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
charge = cos(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
return {'pos':(x,y), 'displacement': displacement, 'charge': charge}
#go left along bottom transmission line
x = path_length - howfar - pad
y = tl_open_bot_y + d
displacement = -sin(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
charge = -cos(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
return {'pos':(x,y), 'displacement': displacement, 'charge': charge}
def e_path_short(param, time):
"""Same as e_path_open(...) above, but for the short-circuit line."""
# d is a vertical offset between the electrons and the wires
d = e_radius + 2
# pad is how far to extend the transmission line beyond the image borders
# (since those electrons may enter the image a bit)
pad = 36
path_length = (2 * (tl_length + pad) + 4*d
+ (tl_short_bot_y - tl_short_top_y - tl_thickness))
howfar = param * path_length
#at the beginning, go right along top wire
if howfar < tl_length + pad:
x = howfar - pad
y = tl_short_top_y + tl_thickness - d
displacement = cos(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
charge = sin(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
return {'pos':(x,y), 'displacement': displacement, 'charge': charge}
#at the end, go left along bottom wire
if (path_length - howfar) < tl_length + pad:
x = path_length - howfar - pad
y = tl_short_bot_y + d
displacement = cos(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
charge = -sin(2 * pi * (tl_length - x) / wavelength) * cos(time)
return {'pos':(x,y), 'displacement': displacement, 'charge': charge}
#in the middle...
charge = 0
displacement = cos(time)
#top part of short...
if tl_length + pad < howfar < tl_length + pad + d:
x = howfar - pad
y = tl_short_top_y + tl_thickness - d
#bottom part of short...
elif tl_length + pad < (path_length - howfar) < tl_length + pad + d:
x = path_length - howfar - pad
y = tl_short_bot_y + d
#vertical part of short...
else:
x = tl_length + d
y = (tl_short_top_y + tl_thickness - d) + ((howfar-pad) - (tl_length + d))
return {'pos': (x,y), 'displacement': displacement, 'charge': charge}
def e_path(param, time, which):
return e_path_open(param, time) if which == 'open' else e_path_short(param, time)
def main():
#Make and save a drawing for each frame
filename_list = [os.path.join(directory_now, 'temp' + str(n) + '.png')
for n in range(frames_in_anim)]
for frame in range(frames_in_anim):
time = 2 * pi * frame / frames_in_anim
#initialize surface
surf = pg.Surface((img_width,img_height))
surf.fill(bgcolor);
#draw transmission line
pg.draw.rect(surf, wire_color, [0, tl_open_top_y, tl_length, tl_thickness])
pg.draw.rect(surf, wire_color, [0, tl_open_bot_y, tl_length, tl_thickness])
pg.draw.rect(surf, wire_color, [0, tl_short_top_y, tl_length, tl_thickness])
pg.draw.rect(surf, wire_color, [0, tl_short_bot_y, tl_length, tl_thickness])
pg.draw.rect(surf, wire_color, [tl_length,
tl_short_top_y,
tl_thickness,
tl_short_bot_y - tl_short_top_y + tl_thickness])
#draw line down the middle
pg.draw.line(surf,split_line_color, (0,img_height//2),
(img_width,img_height//2), 12)
#draw electrons. Remember, "param" is an abstract coordinate that goes
#from 0 to 1 as the electron position goes right across the top wire
#then left across the bottom wire
equilibrium_params = linspace(0, 1, num=num_electrons)
for which in ['open', 'short']:
for eq_param in equilibrium_params:
temp = e_path(eq_param, time, which)
param_now = eq_param + max_e_displacement * temp['displacement']
xy_now = e_path(param_now, time, which)['pos']
pg.draw.circle(surf, ecolor, tup_round(xy_now), e_radius)
#draw arrows
arrow_params = linspace(0, 0.49, num=num_arrows)
for which in ['open', 'short']:
center_y = tl_open_center_y if which == 'open' else tl_short_center_y
for i in range(len(arrow_params)):
a = arrow_params[i]
arrow_x = e_path(a, time, which)['pos'][0]
charge = e_path(a, time, which)['charge']
head_y = center_y + max_arrow_halflength * charge
tail_y = center_y - max_arrow_halflength * charge
draw_arrow(surf, arrow_x, tail_y, head_y)
#shrink the surface to its final size, and save it
shrunk_surface = pg.transform.smoothscale(surf, (final_width, final_height))
pg.image.save(shrunk_surface, filename_list[frame])
seconds_per_frame = animation_loop_seconds / frames_in_anim
frame_delay = str(int(seconds_per_frame * 100))
# Use the "convert" command (part of ImageMagick) to build the animation
command_list = ['convert', '-delay', frame_delay, '-loop', '0'] + filename_list + ['anim.gif']
subprocess.call(command_list, cwd=directory_now)
# Earlier, we saved an image file for each frame of the animation. Now
# that the animation is assembled, we can (optionally) delete those files
if True:
for filename in filename_list:
os.remove(filename)
main()
Legendas
Adicione uma explicação de uma linha do que este ficheiro representa
Elementos retratados neste ficheiro
retrata
Um valor sem um elemento no repositório Wikidata
11 novembro 2014
Histórico do ficheiro
Clique uma data e hora para ver o ficheiro tal como ele se encontrava nessa altura.
| Data e hora | Miniatura | Dimensões | Utilizador | Comentário | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| atual | 02h10min de 29 de maio de 2016 | 300 × 110 (105 kB) | Sbyrnes321 | all arrows are now red, to reduce image complexity | |
| 04h12min de 12 de novembro de 2014 | 300 × 110 (155 kB) | Sbyrnes321 | User created page with UploadWizard |
Utilização local do ficheiro
A seguinte página usa este ficheiro:
Utilização global do ficheiro
As seguintes wikis usam este ficheiro:
- ca.wikipedia.org
- cs.wikipedia.org
- en.wikipedia.org
- id.wikipedia.org
- it.wikipedia.org