Usuário:Cabral.bh/Rascunho do artigo ABNT 14.136
ABNT 14.136 é a norma brasileira para plugues e tomadas.
O web site "Plus Mundiais" da Comissão Eletrotécnica Internacional (IEC), chama este plugue de Tipo N.[1]
Descrição[editar | editar código-fonte]




O plugue utilizado no Brasil tem três pinos redondos dispostos triangularmente em uma base hexagonal, sendo o pino central o pino terra, e 2 capacidades de condução de corrente elétrica.
As dimensões dos pinos para a variante de 10A são 4,0 mm (0,16 in) de diametro e 19,0 mm (0,75 in) de comprimento.
Para a variante de 20A, as dimensões dos pinos são 4,8 mm (0,19 in) de diametro e 19,0 mm (0,75 in) de comprimento.
O pino terra é deslocado do eixo de alinhamento dos pinos de neutro e terra em 3,0 mm (0,12 in).
Opcionalmente os pinos de fase e nutro podem ter uma capa protetora contra contatos acidentais de 10,0 mm (0,39 in). Estas capas são opcionais pois as tomadas tem dispositivos que tornam este artificio desnecessário para a proteção contra contatos.
Existe a versão do plug sem o pino terra para utilização de equipamentos Classe de isolamento:classe II classe II de isolamento
A tomada tem de ter um poço de 10,0 mm (0,39 in) de profundidade e uma superfície protetora em seu perímetro de no minimo 20,0 mm (0,79 in) ou um poço de 12,0 mm (0,47 in) sem superfície protetora. esta construção tem o objetivo de evitar contatos acidentais durante a inserção do plug e evitar também a inserção monopolar do plug, o que gera uma situação insegura para o usuário.
A disposição dos contatos na tomada é tal que o contato do pino terra faz contato antecipadamente em relação aos contatos de fase e neutro, garantindo que o equipamento seja aterrado antes de ser energizado.
As tomadas não tem como requisito a obrigatoriedade de obturadores de segurança contra inserção de objetos.
There are unearthed versions of the plug used with this outlet having only the two flat inverted V-aligned pins, without the Earthing pin. Such plugs are only to be used for devices where other safety standards are in use (e.g. double insulation) and these plugs are rated at a maximum of only 7.5 amps. They are not available separately but only integrally with power cords specifically designed for the purpose.
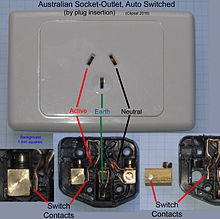
A view of the Wiring Side of a typical dual socket-outlet is also shown on the right, together with an annotated view of the mechanism, without the front cover. (One "Rocker" switch has been disassembled to show its operation.)
If required, such dual socket-outlets now can be obtained (at additional cost) utilizing insulation displacement as a means of connecting to the supply conductors, as can be seen in the illustration - below right.[2][3] The benefits claimed for their use in these applications include up to 50 percent faster installation, due to the reduction in the stripping, twisting and screwing down processes.
Switch Requirements[editar | editar código-fonte]

Regulations state that “Each socket-outlet shall be individually controlled by a separate switch that .... operates in all active conductors.” [4]
However, this clause has three “exceptions”, which state:-
“A single switch may be used for the control of two socket-outlets located immediately adjacent to each other.”
(subject to the current rating of the switch to be at least equal to the
(a) total current rating of the sockets concerned; or
(b) the current rating of the overcurrent protection device concerned, whichever is the lesser value.)[5]
“A socket-outlet that is switched by the insertion and withdrawal of the plug shall be deemed to meet the requirements ....” (Such a socket-outlet and the mechanism used is shown on the left.)
”A socket-outlet that is rated at not more than 10 A, installed for the connection of a fixed or stationary appliance or a luminaire and that is not readily accessible for other purposes, need not be controlled by a switch.” (Such a socket-outlet and plug, installed in a ceiling space, is shown below on the right.)
However, "stationary appliances" (such as fans) and most “luminaires” would normally be controlled by a remote switch, which would switch the supply via the socket-outlet concerned. Exceptions could be devices such as illuminated “Exit” signs, which require connection to the power supply at all times.
It should be noted that “Each switch or means of operating a switch, for a socket-outlet shall be –
(a) As close as practicable to the socket-outlet: and
(b) Marked to indicate the socket-outlet(s) or the connected electrical equipment that it controls.
(Exception: Marking is not required where the socket-outlet controlled is obvious because of the location of the switch.)” [6]
Double Pole switches are required in Caravans and Mobile Homes:-
"All switches that are installed in transportable structures and intended to be connected to the site supply shall operate in all live (active and neutral) conductors." [7]
"Switches that directly control socket-outlets shall comply with the above requirements." [8]
Variants[editar | editar código-fonte]
Standard single phase 230 V domestic socket outlets in Australia and New Zealand are usually rated at 10 A.
However, for heavier duty applications there are several variants having current ratings of up to 32 A.
The 15 A outlet has a wider Ground pin than the 10 A outlet.
The 20 A outlet has a wider Ground pin and wider Line and Neutral pins.
The 25 A outlet has an inverted "L"shaped Ground pin and wider Line and Neutral pins.
The 32 A outlet has a sideways "U" shaped Ground pin and wider Line and Neutral pins. From this it may be seen that any plug can be inserted into an outlet of the same or higher rating but cannot be inserted into an outlet of lower rating.
Hence, a 10 A plug will fit into all of the five types of outlets, a 15 A plug will fit into all except a 10 A (and so on) while a 32A plug will fit only into a 32A outlet.
In general, only 10 A and 15 A outlets are likely to be encountered in domestic or commercial installations. Higher rated outlets may be encountered in some industrial installations.
A variant of the Australian standard 10 amperes plug has a socket on the back to allow connection of a second appliance to the same outlet. This type of plug is known officially as a "socket adapter plug" but is referred to colloquially, in Australia, as a "piggy-back plug" or, in New Zealand, as a "tap-on" plug. In Australia the plug is now available only as part of a pre-assembled extension cord, or by special order. In New Zealand rewirable PDL 940 "tap-on" plugs are more widely available.

Other variants include plug/sockets with a rating of 10 A utilising a round earth pin, which is used on "special use" circuits, such as storage heaters in classrooms; and a 110 V 10 A version that has round active & neutral pins with a flat earth pin. The latter is rated at only 110 V (since certain [foreign] 110 V plugs could be inserted into the Socket-Outlet) and may be used on PAR 64 lights, where two 110 volt 1000 Watt lamps are used in series.[9]
The active terminal of the Plug is the first pin from the Earth pin in a clockwise direction when viewed from the wiring side. Likewise, it is the first 'socket' from the Earth 'socket' in a clockwise direction when viewing the front of a socket-outlet. Care should be taken if Argentinian standards or faulty wiring swaps the active and neutral pins. Care also should be taken with the 10 A version with the round pin as physically compatible, but electrically incompatible NEMA 7–15 connector used for 277 V 15 A connections is encountered in commercial or industrial settings in the Americas.[10]
The Chinese CPCS-CCC (Chinese 10 A/250 V) plugs and socket-outlets are almost identical, differing by only 1 mm longer pins[11] and installed "upside down". Note that whilst AS 3112 plugs will physically connect, they may not be electrically compatible to the Chinese 220 V standards.
Originally there was no convention as to the direction of the Earth pin. Often it was facing upwards, as socket-outlets in China now do but it could also be downwards or horizontal, in either direction.[12] The pin orientation was codified in the 1950s with the Earth pin required to face downwards{{carece de fontes}}, so that the longer Earth pin will be the last to lose contact if the inserted plug is tugged downwards. If products destined for the Chinese market are exported, the bottom entry plug becomes a top entry plug, and the customer will often take advantage of the situation by suspending the power cord upwards.
Origins[editar | editar código-fonte]

Australia's standard plug/socket system was originally codified as standard C112 (floated provisionally in 1937, and adopted as a formal standard in 1938), which was superseded by AS 3112 in 1990.
While in 1937 there was no "Standards Australia" in existence, it was then that the design was adopted as a result of a "Gentlemen's Agreement" between manufacturers Fred Cook of Ring-Grip, Geoffrey Gerard of Gerard Industries and Brian Harper Miller of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV).[13]
The design was based on an American plug and socket-outlet intended for use at 120 V which was patented in 1916 under US patent 1,179,728.[14] Australian plugs will fit these obsolete American outlets perfectly. (While this socket-outlet never became a NEMA standard design, the 50 A NEMA 10-50R, has a similar pin configuration in a larger form.[15]) Argentina, Uruguay and China based their plugs and sockets on the same design. New Zealand also adopted the Australian design, since Australian equipment and many electrical appliances were exported to that country.
One of the reasons behind the adoption of that particular design was that it was cheap to make; the flat pins could be easily stamped out of sheet brass, in contrast to round pins or thicker rectangular ones used in other countries. This was also a consideration when the Chinese authorities officially adopted the design in relatively recent times, despite the considerable inroads the British plug had made, due to its use in Hong Kong. The Chinese socket is normally mounted with the earth pin at the top. This is considered to offer some protection should a conductive object fall between the plug and the socket [16] [17]
However, a major update AS/NZS 3112:2000 was released in 2000. This mandated active and neutral insulated pins[18] on the plugs sold for use with these socket-outlets as from 3 April 2005, which somewhat negates any 'advantage' of having the earth pin uppermost. The standard AS/NZS 3112:2004 introduced more stringent testing procedures to test for bending of the pins and subtle changes to the radius of the pin tips. The current version is AS/NZS 3112:2011, Approval and test specification—Plugs and socket-outlets.
Voltage[editar | editar código-fonte]
The nominal voltage in most areas of Australia was set at 240 V in the 1920s. However, a change began in 1980 with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) deciding to rationalise the 220 V, 230 V and 240 V nominal voltage levels around the world to a consistent 230 V.
This rationalisation was ostensibly made to improve the economics of making appliances by allowing manufacturers to produce a range of items with a rated voltage of 230 V. In 2000, Standards Australia issued a system Standard, AS60038, with 230 V as the nominal voltage with a +10% to –6% variation at the point of supply. (253 V to 216.2 V)
A new power quality standard, AS61000.3.100, was released in 2011[19] that details requirements additional to the existing systems Standard. The new Standard stipulates a nominal 230 V, and the allowable voltage to the customer’s point of supply is, as mentioned, +10% to –6%. However, the preferred operating range is +6% to –2%. (243.8 V to 225.4 V) [20]
Brazil[editar | editar código-fonte]
In Brazil, this kind of plug is commonly found in high-power appliances like air conditioners, dishwashers, and household ovens. The reasons why they have been unofficially adopted for this use may be the robustness and high-current bearing capabilities, the impossibility of inverting phase (active) and neutral pins, or the fact that Argentina, a border country, uses this plug and used to be more developed than Brazil in the past so there may have been a flux of high-powered appliances from Argentina to Brazil at some point in time.{{carece de fontes}}
Nowadays, Brazil has adopted the national standard NBR 14136, which is loosely based on the IEC 60906-1 standard. NBR 14136 defines two types of socket-outlets and plugs: one for 10 A, with a 4 mm pin diameter, and another for 20 A, with a 4.8 mm pin diameter. New apparatus has been sold with the new plug, so the tendency is the usage of the "Australian" plug to fade away.
References[editar | editar código-fonte]
- ↑ «IEC - World Plugs: Plug Type I». iec.ch. Consultado em 07 Janeiro 2018 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ «Quick Connect» (PDF). Updates.clipsal.com. Consultado em 19 de abril de 2017
- ↑ «Page Not Found - Clipsal by Schneider Electric». clipsal.com.au. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ AS/NZS 3000:2007 (Wiring Rules) - 4.4.4.1
- ↑ AS/NZS 3000:2007 (Wiring Rules) - 4.4.4.2
- ↑ AS/NZS 3000:2007 (Wiring Rules) - 4.4.4.3
- ↑ AS/NZS3001:2008 (Electrical Installations – Transportable structures and vehicles) - 3.6.2
- ↑ AS/NZS3001:2008 (Electrical Installations – Transportable structures and vehicles) - 3.6.3.1
- ↑ «Plugs, Sockets and Adaptors Technical Data - 621471» (PDF). Updates.clipsal.com. Consultado em 19 de abril de 2017
- ↑ «NEMA Straight Blade Reference Chart». stayonline.com. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ «International Standards Reference Chart». stayonline.com. 20 January 2016 Verifique data em:
|data=(ajuda) - ↑ Hunter, John. «The origins of the Australian plug». iinet.net.au. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ «Electrical Power Connector Overview in Australia» (PDF). Ewh.ieee.org. Consultado em 19 de abril de 2017
- ↑ «Patent Images». uspto.gov. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ «Plug and Receptacle Configurations: NEMA Straight Blade Plugs and Receptacles». Frentz & Sons Hardware. Consultado em 21 de janeiro de 2016
- ↑ http://www.plugsocketmuseum.nl/Australian1.html
- ↑ «History of the Australian plug». electrical-contractor.net. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda) - ↑ «Pins on plug tops» (PDF). Commerce.wa.gov.au. Consultado em 19 de abril de 2017
- ↑ AS 61000.3.100-2011 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Limits - Steady state voltage limits in public electricity systems, Standards Australia, 2011
- ↑ «When voltage varies - Electrical connection». electricalconnection.com.au. Consultado em 19 April 2017 Verifique data em:
|acessodata=(ajuda)
External links[editar | editar código-fonte]
Category:Mains power connectors
Category:Standards of Australia and New Zealand

